
Eritrea
Brief Overview
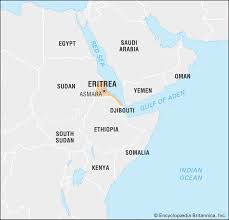
Eritrea is a northeast African country on the Red Sea coast. It shares borders with Ethiopia, Sudan and Djibouti. The capital city, Asmara, is known for its Italian colonial buildings, like St. Joseph’s Cathedral, as well as art deco structures. Italian, Egyptian and Turkish architecture in Massawa reflect the port city’s colorful history. Notable buildings here include St. Mariam Cathedral and the Imperial Palace.
Political Context
Eritrea is small, coastal country strategically located along the Red Sea in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Sudan, Ethiopia and Djibouti. Eritrea is divided into six administrative regions called ‘zobas’, which vary in size, population and socioeconomic conditions.
After a long liberation war, Eritrea regained self-rule in 1991 and full independence in 1993. The country enjoyed seven years of stabilization, reconstruction and development, before the onset of a border war with Ethiopia in 1998. The brunt of hostilities ended in 2000 and a UN Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC) ruled in favor of Eritrea in 2002, but the border zone remained militarized, UN Security Council sanctions were imposed in 2009 and reinforced in 2011. Eritrea remained in a state of mobilization for almost two decades under transitional political arrangements focused on national security with a suspension of traditional checks and balances. The earlier development model was eschewed in favor of greater self-reliance and a more state-led planned economy.
Management of national resources – labor, land, and finance – was geared toward maintaining a state of military readiness, alongside efforts to broaden social equity. The private sector was gradually replaced by an extensive state sector geared to marshal scarce resources and increasing restrictions were imposed. An institutional framework developed to direct labor into an indefinite military and national service. The resulting austerity and extensive controls spurred migration of people and capital.
In mid-2018, Eritrea experienced a turnaround in its external environment. Ethiopia accepted the EEBC decision and signed a peace treaty with Eritrea in July 2018. Eritrea began to normalize relations with neighboring countries. In November 2018, UN Security Council lifted its sanctions on Eritrea. This raised expectations of a reorientation of Eritrean political and economic arrangements have been met with caution from the administration, as evidenced by President Isaias’ recent call for a “patient appraisal of the unfolding reality.”
Economic Overview
Eritrea’s recent growth performance has been marked by significant volatility in part due to its dependence on a predominantly rain-fed agriculture sector, accounting for about one-third of the economy (and which has a significant impact on distribution services which account for around 20% of gross domestic product (GDP), and on a narrow mining sector which also accounts for 20% of the economy. Real GDP growth is estimated to have recovered to around 12% in 2018, while averaging -2.7% during 2015-18 on account of frequent droughts and a decline in mining production.
Reported inflation has been negative during 2016-18, following the exchange of currency in circulation in November 2015 that resulted in a monetary contraction. Deflation continued in 2018 as increased trade with Ethiopia resulted in further put downward pressure on prices.
In recent years, Eritrea has significantly tightened fiscal policy to reverse the chronic deficits it suffered after the increase in regional insecurity in 1998. In 2018, the fiscal surplus widened to around 11% of GDP in 2018. This was largely achieved by a sharp drop in capital spending as well as some revenue measures. However, fiscal pressures, both recurrent and wage-related are likely to mount.
Short-term growth prospects remain challenging given fiscal constraints and limited opportunities under existing restrictions. The recovery in agriculture is expected to slow. The country remains in a difficult macroeconomic situation with an unsustainable debt burden (including arrears to the World Bank) and vulnerable financial and external sectors.
However, the economic outlook is potentially favorable in the medium term, reflecting the new mining operations coming on stream, but are also dependent on measures to relax restrictions on the private sector imposed and to reopen access to concessional development finance.
Poverty appears to have remained widespread in Eritrea, but the lack of data limits available quantitative evidence. The most recent available survey data from 1996/97 indicate a 70% poverty rate.
The country has seen consistent improvements in life expectancy (rising from 50 years in 1990 to 65 years in 2015) and expected years of schooling (from 3.8 years in 1995 to 5.4 years in 2010) and strong social outcomes in the face of limited resources.
Nevertheless, challenges remain. An unfinished maternal and child health agenda is compounded by a significant rise in Non-Communicable Disease (NCDs). Skilled birth attendance remains low, between 35-60%, maternal mortality ratio high at 485 deaths per 100,000 live births and under-five malnutrition also high with 52% of children underweight.

The State of Eritrea
Capital: Asmara
Population: 5.6 million
Area: 117,400 sq km (45,300 sq miles)
Major languages: Tigrinya, Tigre, Arabic, English
Major religions: Islam, Christianity
Life expectancy: 63 years (men), 67 years (women)
Currency: Nakfa
UN, World Bank

Physical Contacts of the Presidency
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Prime Minister’s Office
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the National Assembly
Name of Speaker of the House:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Chief Of State and Cabinet Ministers
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Ministry of Interior
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax
Physical Contacts of the Ministry of Justice
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Ministry of Women’s Affairs
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the National Human Rights Commission
Name of Minister:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Police
Name of Inspector General:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Physical Contacts of the Military
Name of Inspector General:
Address:
Telephone:
Fax:
Important Information of Key Human Rights Issues in Eritrea
Number Prisons in Eritrea
Number Prisoners in Eritrea
Secret Detention Centres:
Police Stations in Eritrea
What are the current and ongoing human rights issues in Eritrea
(1) Freedom of the Press
(2) Human Rights Defenders Issues
(3) Impunity
African Union (AU)
Joined the OAU
Signed the Constitutive Act of The African Union on:
Ratified:Instrument Deposited:
Signed:
Ratified:
Instrument Deposited:
Signed:
Ratified:
Instrument Deposited:
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
4.Protocol on Amendments to the Protocol on the Statute of the African Court of Justice and Human Rights
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –
Signed: –
Ratified: –
Instrument Deposited: –